What is ta-C diamond coating? #
ta-C diamond coating, i.e. tetrahedral amorphous carbon (tetrahedral amorphous carbon) coating, is a kind of diamond-like coating (DLC), which belongs to hydrogen-free DLC coating. Its microhardness can reach 3000 - 8500hv.
When ta-C microhardness exceeds 7500 HV, its various material properties are very close to those of natural diamond. We are used to call it diamond coating. Unlike CVD, which is a high-temperature, high-pressure deposition technique at 900°C, the NanoLion ion source, ta-C, allows for the deposition of perfect diamond coatings at 80°C, with high bonding strength and largely independent of the type of material.
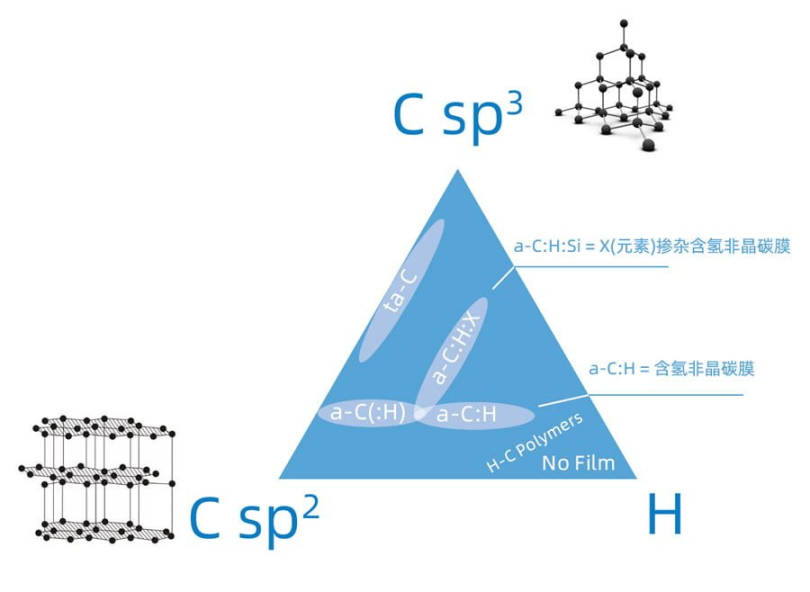
Ideal materials, graphite is a planar structure, 100% of sp2; diamond is a three-dimensional structure, 100% of sp3. and DLC is a hybrid of sp2 and sp3. Usually said DLC coating, for the black and gray high sp2 content of carbon film, 10-20% of hydrogen content. Typically ta-C coating, a carbon film with sp3 content over 30%.
Nash Diamond Coating #
Nasi Diamond Coating is a high hardness DLC with sp3 content more than 80% prepared by over-arcing technology, which has passed the BAG test, Double 85 48h test, Steel Velvet friction test, and Corrosion test. It can be widely used in the modification of ITO glass, super thermal conductive glass and other sub-metal materials.
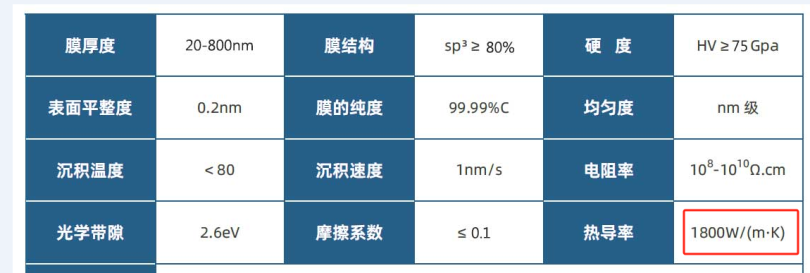
The ta-C membrane has a high thermal conductivity, personally favoring a value of 1000 W/m.k due to the membrane structure. But it is still substantially higher than ordinary materials.
At film thicknesses below 20 nm, ta-C coatings, even in the blue-off region, still have higher visible light transmittance than 90%. Due to the coating preparation process and time cost limitations, the PVD method cannot prepare thick diamond coatings. While CVD process can.
| substrates | white glass | |
| No. | Before Coating After Coating | |
| 1 | 94% 91% | |
| 2 | 94% 91% | |
| 3 | 94% 92% | |
| 4 | 94% 91% | |
| 5 | 94% 91% |
Low-temperature, high-energy deposition #
The production rate, R, of diamond films is determined solely by the C+ ion flux. And the low-temperature, high-ion-energy deposition mode requires the support of a power supply that produces high current densities greater than a few milliamperes per square centimeter.
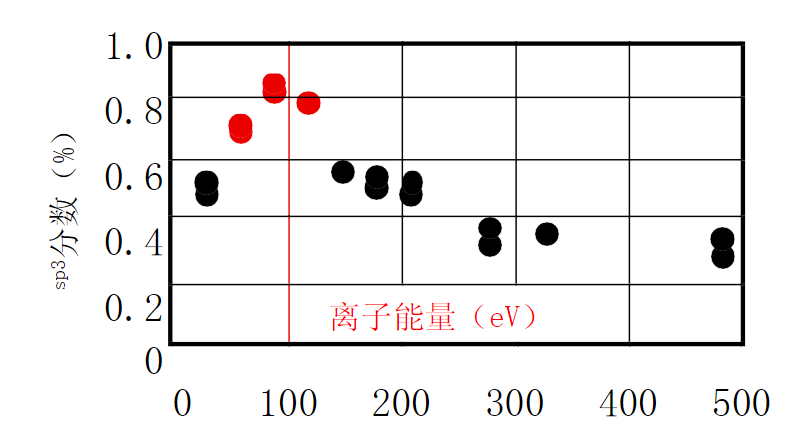
The sp3 bond content, which can be obtained at energies of 100 ev, is extremely large, about 851 TP3T.
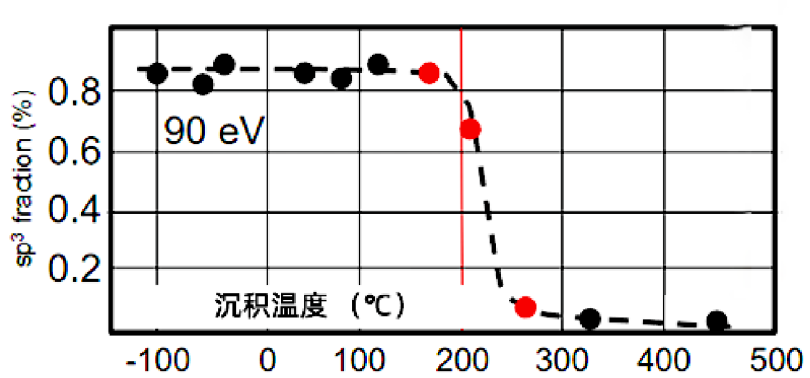
sp3 bond content, which decreases above 150°C.
Nash Bend Filter Arc Technology #
Bent tube magnetic filtration vacuum cathodic arc ion plating device, through the straight tube plus bent tube design, can realize efficient removal of impurities and large particles in the plasma, and can deposit low surface roughness and more perfect membrane materials. However, since the elbow filters out more than half of the particles and ions, the membrane deposition rate is significantly lower. Better filtration means lower deposition efficiency.
As a result, Naxi is using non-filtered arc ta-C more extensively to achieve a balance of coating quality and capacity.
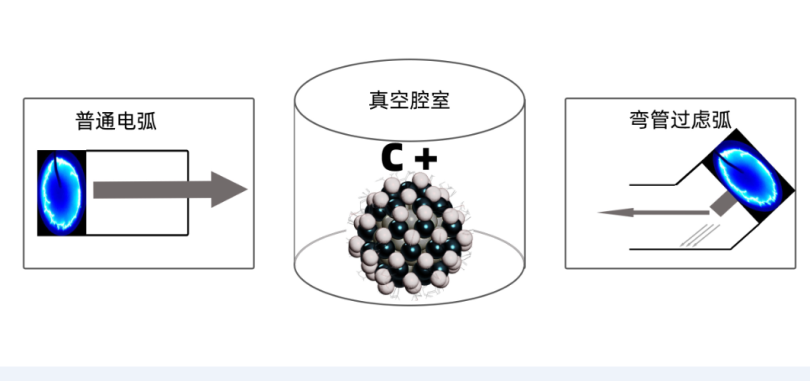
NanoLion enables multi-stage bend filtration, resulting in highly controllable diamond films with low growth defects. For ultra-thin coatings of 10-20nm, lower defect rates are required to ensure film product yields.
Multilayer composite structure of ta-C #
Nasi ta-C is usually a composite film structure, with Cr, Ti and other metal priming layer to increase the bonding force with the substrate, ta-C: X transition layer, sp3/sp2 low ratio layer, and sp3/sp2 high ratio layer composition.
As the sp3 content increases, the density and compressive stress of the membrane material increases linearly, and a multilayer structure is needed to overcome the high stress of the superhard membrane. If ultra-thick ta-C membranes need to be made, a ta-C:Xta-C stacked layer design is required.
The ta-C, like other DLC coatings, is highly customizable.
Some measurements on ta-C ultrathin films #
It should be noted that the current sp3 content is a relative test method, such as the Raman test. We are not able to measure the absolute content of sp3 very accurately.
We also cannot accurately measure the hardness of ta-C diamond films because the film thickness is less than 1 micron. We usually infer the hardness of the film based on the ratio of sp3. And for ordinary ta-C thick film, we can visually measure the microhardness of the film.
Adhesion test #
| makings | Film thickness (nm) | Critical load (N) |
| fiberglass | 20 | 30 |
| resinous | 20 | 25 |
| high speed steel | 200 | 75 |
Other Tests #
- 5% salt spray test: 120h
- Double 85 test: 48h
- 1KG Eraser test: 5000 times
- Visible light transmission test: 90% or above
- Cytotoxicity test: In compliance with the requirements of ISO10993-5 and GB/T16886.5 standards, using tetramethyl azole salt trace enzyme reaction colorimetric method (MTT method): the cytotoxicity is grade 0, and its cytotoxicity is slightly lower than that of pure titanium.
- Hemolysis test: according to the standard of YY/T0127.1-93, the hemolysis rate of graphite powder group is 3.08%, which is a non-hemolytic material;
Application of ta-C #
In most cases, different thicknesses of ta-C correspond to different areas of application. As for ultra-thick films above 10 microns, microhardnesses higher than 3000 HV usually require post-treatment.
ta-C diamond coating with the following excellent material properties: High thermal conductivity Chemically stable High modulus of elasticity High hardness and abrasion resistance Sputtering resistance Extremely high carrier mobility (electrons and holes) Large forbidden bandwidths Low fugitive power UV sensitivity (absorption) Infrared penetration High electrical resistivity High dielectric constant High breakdown point Hydrogen-free Ultra-thin Negative electron affinity potentials (wide optical bandgap) Fast propagation of sound waves with high fidelity Thermal shock resistance Bacteriostatic Self-cleaning
Nanoscale optically modified film (high transmittance) #
- ITO protective film
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Device Window (Infrared Transparency Enhancement)
- X-ray window (high transmission, radiation resistant)
- CO2 laser window
- High-speed Interceptor Missile cowling
- UV or radiation sensors
Thermal Conductive Film (High Thermal Conductivity) #
- High Power and High Frequency Devices
- Transparent Thermal Conductive Film for Glass
- Heat dissipation film for optoelectronic devices
- Heat sinking of high frequency and microwave devices
- temperature sensor
acoustical #
- speaker cone
- Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) [High Bandwidth (4GHZ-6GHZ) Filters
Wear-resistant decorative plating #
Superhard Tool Coating #
- PCB microdrill and gong cutter
- 12% High Silicon Aluminum Alloy Processing; Copper, Silver, Gold and other non-ferrous metal processing;
- Woodworking Knives, Acrylic CNC Cutting Tools
- Razors, film slicers
- High-end Kitchen Knife
Ultra-hard lubrication coating (non-toxic to humans, biocompatible, wear-resistant and self-lubricating) #
- Implanted medical devices: artificial joints, dentures, dental trays
- high-frequency electric knife
Automobile spare parts #
Comparison of the properties of various diamond films with those of natural diamonds #
Nano lion diamond film, for 10-800nm ultra-thin ultra-hard (greater than 4000HV for ultra-hard coating).
- Deposition temperature: 80°C for ta-C; usually above 900°C for CVD method;
- Film thickness: ta-C method is usually in the nanometer range, diamond method theoretically has no thickness limit; on tools such as microdrills, it is usually 5-10 microns;
- Crystal structure: ta-C is tetrahedral amorphous; CVD is single or polycrystalline structure.
- Hardness: CVD diamonds are harder, allowing the creation of defect-free diamond materials
- Application areas: ta-C is usually used for ultra-thin protection or thermal conductivity, due to the low deposition temperature, not subject to substrate limitations, is divided into ultra-thin optical modified film and ultra-hard self-lubricating modified film. And CVD is usually used for carbide cutting tools, high-end decorations, etc. due to high temperature and size limitation;
| characterization | Natural Diamond | CVD | DLC (a:CH) | ta-C |
| Hardness (Gpa) | 100 | 80 - 100 | 10 - 50 | 80 - 100 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.5 | 3.2 - 3.4 | 1.7 - 2.2 | 3.0 - 3.2 |
| coefficient of friction | 0.1 | 0.1 (Polished) | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| roughness | - | 3µm | optical smoothing | optical smoothing |
| adhesion | - | lower (one's head) | center | your (honorific) |
| deposition temperature | - | >600° C | 120° C - 325° C | 80° C - 150° C |
| framework | crystallize | crystallize | amorphous | amorphous |
| reactive gas | - | YES | YES | selectable |
| temperature resistance | - | 600° C+ | 250° C - 350° C | 500° C+ |
Nash P Series DLC Vacuum Coating Equipment #
Naxion's P-Series consists of three deposition processes, PeCVD, Ion Source and Composite Deposition.
 Naxau Vacuum Coating Processing - Naxau AM
Naxau Vacuum Coating Processing - Naxau AM
